wafer meaning semiconductor|A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Semiconductor Wafers : Cebu In the semiconductor industry, the term wafer appeared in the 1950s to describe a thin round slice of semiconductor material, typically germanium or silicon. The round shape characteristic of these wafers comes from single-crystal ingots usually produced using the Czochralski method. Silicon . Tingnan ang higit pa CH4KNU SCANDAL VIRAL Julliene Dayao Look a LIKE Part 2. Pinay Atabs Gusto na Ma Pwetan. Pinay Bessy Sex Scandal. Sobrang Sikip na atabs. Atabs Gusto na Magka Baby. YoYo Chan Nude Video Finger Selfie. Carren Rasco Scandal. Sarap na Sarap si Girlfriend sa Sex. Bacolod Sex SCandal Viral.
PH0 · What is a semiconductor? An electrical engineer explains how the
PH1 · What is a semiconductor? An electrical engineer
PH2 · What is a Wafer?
PH3 · What is a Semiconductor Wafer?
PH4 · Wafer (electronics)
PH5 · Wafer
PH6 · The Different Types of Semiconductor Wafers
PH7 · Semiconductor Wafer – Overview and Facts
PH8 · Manufacturing: From Wafer to Chip
PH9 · Chips and Wafers: What's the Difference?
PH10 · A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Semiconductor Wafers
Add an ergonomic lift to your monitor — and do even more with extra shelf space on your desk. Fits perfectly across the cable tray opening on your Secretlab MAGNUS, while retaining full access to the rear hinged cover. . Metal Desk Top Construction: MDF, High-Pressure Laminate Bamboo with Steel (SPCC) Cable Management Tray Yes Package Size
wafer meaning semiconductor*******What is a Semiconductor Wafer? | WaferProWafer (electronics) - Wikipedia
A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Semiconductor WafersWafer (electronics) - WikipediaA Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Semiconductor Wafers
In the semiconductor industry, the term wafer appeared in the 1950s to describe a thin round slice of semiconductor material, typically germanium or silicon. The round shape characteristic of these wafers comes from single-crystal ingots usually produced using the Czochralski method. Silicon . Tingnan ang higit paIn electronics, a wafer (also called a slice or substrate) is a thin slice of semiconductor, such as a crystalline silicon (c-Si, silicium), used for the fabrication of integrated circuits and, in photovoltaicsThe . Tingnan ang higit pa
ChallengesThere is considerable resistance to the 450 mm transition despite the possible productivity improvement, because of concern . Tingnan ang higit paWhile silicon is the prevalent material for wafers used in the electronics industry, other compound III-V or II-VI materials have also been employed. Gallium arsenide (GaAs), a III-V semiconductor produced via the Czochralski method, gallium . Tingnan ang higit paFormationWafers are formed of highly pure, nearly defect-free single crystalline material, with a purity of 99.9999999% (9N) or higher. One . Tingnan ang higit paStandard wafer sizesSiliconSilicon wafers are available in a variety of diameters from 25.4 mm (1 inch) to 300 mm (11.8 . Tingnan ang higit pawafer meaning semiconductor A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Semiconductor WafersIn order to minimize the cost per die, manufacturers wish to maximize the number of dies that can be made from a single wafer; dies always have a square or rectangular . Tingnan ang higit pa• Die preparation• Epitaxial wafer• Epitaxy• Monocrystalline silicon• Polycrystalline silicon Tingnan ang higit pa In the electronics jargon, a thin slice of semiconductor material is called as a wafer. It could be a silicon crystal which is used in the making of integrated circuits and . What are Wafers? A semiconductor wafer refers to a thin slice of semiconductor material, usually crystalline silicon obtained from sand (Silica) used as .
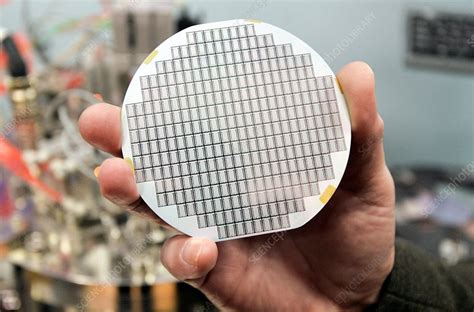
What Does Wafer Mean? A wafer is a piece of silicon (one of the most abundant semiconductors available worldwide) or other semiconductor material, . The starting point for the vast majority of semiconductors is a thin slice of silicon called a wafer. Today’s wafers are the size of dinner plates and are cut from single silicon crystals. Semiconductor wafer properties, such as crystal structure and electrical characteristics, directly influence the performance of the final electronic components. In . Manufacturing: Making Wafers. To make a computer chip, it all starts with the Czochralski process. The first step of this process is to take extremely pure silicon and melt it in a crucible that.Semiconductor wafer is a round piece of silicon which consists of silicon dies that are designed to perform a very specific functionally. One can easily remember from school that silicon has an atomic number of 14 on .
wafer meaning semiconductorDefinition. Semiconductor manufacturing begins with a thin disk of semiconductor material, called a "wafer." A series of processes defines transistors and other structures, .
Semiconductor wafers have multiple applications across different industries. They are widely used in the electronics industry to produce microchips, .
Different types of semiconductor wafers. Semiconductors form the foundation of electronic design and manufacturing. These thin, disc-shaped substrates are not merely components; they are the canvases upon which semiconductor fabrication unfolds. . Phosphorus acts as a donor dopant, meaning additional electrons are added .LM2576T monolithic integrated circuit die. A die, in the context of integrated circuits, is a small block of semiconducting material on which a given functional circuit is fabricated.Typically, integrated circuits are produced in large batches on a single wafer of electronic-grade silicon (EGS) or other semiconductor (such as GaAs) through .
Manufacturing: Making Wafers. To make a computer chip, it all starts with the Czochralski process. The first step of this process is to take extremely pure silicon and melt it in a crucible that .A semiconductor is a material that has an electrical conductivity value falling between that of a conductor, . To get the impure atoms embedded in the silicon wafer, the wafer is first put in a 1,100 degree Celsius chamber. . (a semiconductor in modern meaning) in his Ph.D. thesis in 1910. [39] .
Giving new meaning to the term “wafer-thin” . In the early days of the semiconductor industry, wafers were only three inches in diameter. Since then, wafers have been growing in size, as larger wafers result in more chips and higher productivity. The largest wafer diameter used in semiconductor fabrication today is 12 inches, or .
The process begins with a silicon wafer. Wafers are sliced from a salami-shaped bar of 99.99% pure silicon (known as an 'ingot') and polished to extreme smoothness. . meaning they become stronger and more difficult to dissolve. Positive resist is most commonly used in semiconductor manufacturing because its higher resolution .
The semiconductor industry is a global business today. The leading semiconductor manufacturers typically have facilities all over the world. Samsung Electronics, the world's largest manufacturer of semiconductors, has facilities in South Korea and the US. Intel, the second-largest manufacturer, has facilities in Europe and Asia as well as the US. .Semiconductors work tirelessly behind the scenes to power the world around us – from the technology in your house to the labs curing deadly diseases. They are the foundation of modern technology. Without them, billions of devices across the planet would not function. . Masks are templates used to print circuitry onto a silicon wafer. Mask .Semiconductors are an essential component of electronic devices, enabling advances in communications, computing, healthcare, military systems, transportation, clean energy, and countless other applications. . Next, wafers are printed with highly intricate circuit designs that will later become individual chips. Step 7: Cut Wafer.Since the semiconductor industry is increasingly diversifying into other applications, different types of wafers are used for producing a wide variety of new products.As a result, the humble chuck plate that holds the InP wafer in place throughout the front-end processing is constantly adapting to meet the requirements of various applications.The semiconductor wafer that makes up the IC is fragile and contains numerous intricate connections between its many layers. A combination of these wafers is known as a die. . Today's CPUs and GPUs are .In the microelectronics industry, a semiconductor fabrication plant (commonly called a fab; sometimes foundry) is a factory for semiconductor device fabrication. [1]Fabs require many expensive devices to function. Estimates put the cost of building a new fab at over one billion U.S. dollars with values as high as $3–4 billion not being uncommon. TSMC .Wafer testing is a step performed during semiconductor device fabrication after the back end of line (BEOL) process is finished. During this step, performed before a wafer is sent to die preparation, all individual integrated circuits that are present on the wafer are tested for functional defects by applying special test patterns to them. The wafer testing is .

Step-by-step guide to semiconductor wafer manufacturing at RISE testbed ProNano. Scale up your prototype with nano- and semiconductor technology without having to invest in expensive equipment. . The large capacity of ProNano's MOCVD reactor means that seven 50-millimeter disks can be grown epitaxially in one round, or alternatively one 150 . Wafer Slicing. Once a semiconductor crystal has been grown, it is then sliced into thin wafers using a process known as wafer slicing or wafering. Depending upon the wafer size, the process of slicing involves either wires or blades. . Wet etching is generally isotropic, meaning it removes material uniformly in all directions, which can .A wafer fab is a semiconductor processing facility which turns wafers into integrated circuits. A typical wafer fab employs a series of complex steps to define conductors, transistors, resistors, and other electronic components on the the semiconductor wafer. Imaging steps define what areas will be affected by subsequent physical and chemical .
First of all, let’s further examine one of the challenges posed by the transition from 150mm wafers to 200mm wafers: within-wafer variation. For reasons that are immediately obvious, larger wafers have more within-wafer variation and, therefore require more points of measurement per wafer, especially at the outer edges where yield is .
A semiconductor chip is an electric circuit with many components such as transistors and wiring formed on a semiconductor wafer.An electronic device comprising numerous these components is called “integrated circuit (IC)”. The layout of the components is patterned on a photomask (reticle) by computer and projected onto a semiconductor wafer in the .
The Amsler grid is a quick and simple test that any patient can perform at home. Its purpose is to check the integrity of the central retina, known as the “macula”. The aim of this test is primarily to rule out the development of a disease known as Age-dependent Macular degeneration (AMD). This very simple [.]
wafer meaning semiconductor|A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Semiconductor Wafers